|
|
# 20 | Spring 事务常见错误(下)
|
|
|
|
|
|
你好,我是傅健。
|
|
|
|
|
|
通过上一节课的学习,我们了解了 Spring 事务的原理,并解决了几个常见的问题。这节课我们将继续讨论事务中的另外两个问题,一个是关于事务的传播机制,另一个是关于多数据源的切换问题,通过这两个问题,你可以更加深入地了解 Spring 事务的核心机制。
|
|
|
|
|
|
## 案例 1:嵌套事务回滚错误
|
|
|
|
|
|
上一节课我们完成了学生注册功能,假设我们需要对这个功能继续进行扩展,当学生注册完成后,需要给这个学生登记一门英语必修课,并更新这门课的登记学生数。为此,我添加了两个表。
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. 课程表 course,记录课程名称和注册的学生数。
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
CREATE TABLE `course` (
|
|
|
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
|
|
|
`course_name` varchar(64) DEFAULT NULL,
|
|
|
`number` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
|
|
|
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
|
|
|
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. 学生选课表 student\_course,记录学生表 student 和课程表 course 之间的多对多关联。
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
CREATE TABLE `student_course` (
|
|
|
`student_id` int(11) NOT NULL,
|
|
|
`course_id` int(11) NOT NULL
|
|
|
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
同时我为课程表初始化了一条课程信息,id = 1,course\_name = "英语",number = 0。
|
|
|
|
|
|
接下来我们完成用户的相关操作,主要包括两部分。
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. 新增学生选课记录
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
@Mapper
|
|
|
public interface StudentCourseMapper {
|
|
|
@Insert("INSERT INTO `student_course`(`student_id`, `course_id`) VALUES (#{studentId}, #{courseId})")
|
|
|
void saveStudentCourse(@Param("studentId") Integer studentId, @Param("courseId") Integer courseId);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
2. 课程登记学生数 + 1
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
@Mapper
|
|
|
public interface CourseMapper {
|
|
|
@Update("update `course` set number = number + 1 where id = #{id}")
|
|
|
void addCourseNumber(int courseId);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
我们增加了一个新的业务类 CourseService,用于实现相关业务逻辑。分别调用了上述两个方法来保存学生与课程的关联关系,并给课程注册人数+1。最后,别忘了给这个方法加上事务注解。
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
@Service
|
|
|
public class CourseService {
|
|
|
@Autowired
|
|
|
private CourseMapper courseMapper;
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Autowired
|
|
|
private StudentCourseMapper studentCourseMapper;
|
|
|
|
|
|
//注意这个方法标记了“Transactional”
|
|
|
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
|
|
|
public void regCourse(int studentId) throws Exception {
|
|
|
studentCourseMapper.saveStudentCourse(studentId, 1);
|
|
|
courseMapper.addCourseNumber(1);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
我们在之前的 StudentService.saveStudent() 中调用了 regCourse(),实现了完整的业务逻辑。为了避免注册课程的业务异常导致学生信息无法保存,在这里 catch 了注册课程方法中抛出的异常。我们希望的结果是,当注册课程发生错误时,只回滚注册课程部分,保证学生信息依然正常。
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
@Service
|
|
|
public class StudentService {
|
|
|
//省略非关键代码
|
|
|
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
|
|
|
public void saveStudent(String realname) throws Exception {
|
|
|
Student student = new Student();
|
|
|
student.setRealname(realname);
|
|
|
studentService.doSaveStudent(student);
|
|
|
try {
|
|
|
courseService.regCourse(student.getId());
|
|
|
} catch (Exception e) {
|
|
|
e.printStackTrace();
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
//省略非关键代码
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
为了验证异常是否符合预期,我们在 regCourse() 里抛出了一个注册失败的异常:
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
|
|
|
public void regCourse(int studentId) throws Exception {
|
|
|
studentCourseMapper.saveStudentCourse(studentId, 1);
|
|
|
courseMapper.addCourseNumber(1);
|
|
|
throw new Exception("注册失败");
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
运行一下这段代码,在控制台里我们看到了以下提示信息:
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
java.lang.Exception: 注册失败
|
|
|
at com.spring.puzzle.others.transaction.example3.CourseService.regCourse(CourseService.java:22)
|
|
|
//......省略非关键代码.....
|
|
|
Exception in thread "main" org.springframework.transaction.UnexpectedRollbackException: Transaction rolled back because it has been marked as rollback-only
|
|
|
at org.springframework.transaction.support.AbstractPlatformTransactionManager.processRollback(AbstractPlatformTransactionManager.java:873)
|
|
|
at org.springframework.transaction.support.AbstractPlatformTransactionManager.commit(AbstractPlatformTransactionManager.java:710)
|
|
|
at org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAspectSupport.commitTransactionAfterReturning(TransactionAspectSupport.java:533)
|
|
|
at org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionAspectSupport.invokeWithinTransaction(TransactionAspectSupport.java:304)
|
|
|
at org.springframework.transaction.interceptor.TransactionInterceptor.invoke(TransactionInterceptor.java:98)
|
|
|
at org.springframework.aop.framework.ReflectiveMethodInvocation.proceed(ReflectiveMethodInvocation.java:186)
|
|
|
at org.springframework.aop.framework.CglibAopProxy$DynamicAdvisedInterceptor.intercept(CglibAopProxy.java:688)
|
|
|
at com.spring.puzzle.others.transaction.example3.StudentService$$EnhancerBySpringCGLIB$$50cda404.saveStudent(<generated>)
|
|
|
at com.spring.puzzle.others.transaction.example3.AppConfig.main(AppConfig.java:22)
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
其中,注册失败部分的异常符合预期,但是后面又多了一个这样的错误提示:Transaction rolled back because it has been marked as rollback-only。
|
|
|
|
|
|
最后的结果是,学生和选课的信息都被回滚了,显然这并不符合我们的预期。我们期待的结果是即便内部事务regCourse()发生异常,外部事务saveStudent()俘获该异常后,内部事务应自行回滚,不影响外部事务。那么这是什么原因造成的呢?我们需要研究一下 Spring 的源码,来找找答案。
|
|
|
|
|
|
### 案例解析
|
|
|
|
|
|
在做进一步的解析之前,我们可以先通过伪代码把整个事务的结构梳理一下:
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
// 外层事务
|
|
|
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
|
|
|
public void saveStudent(String realname) throws Exception {
|
|
|
//......省略逻辑代码.....
|
|
|
studentService.doSaveStudent(student);
|
|
|
try {
|
|
|
// 嵌套的内层事务
|
|
|
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
|
|
|
public void regCourse(int studentId) throws Exception {
|
|
|
//......省略逻辑代码.....
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
} catch (Exception e) {
|
|
|
e.printStackTrace();
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
可以看出来,整个业务是包含了 2 层事务,外层的 saveStudent() 的事务和内层的 regCourse() 事务。
|
|
|
|
|
|
在 Spring 声明式的事务处理中,有一个属性 propagation,表示打算对这些方法怎么使用事务,即一个带事务的方法调用了另一个带事务的方法,被调用的方法它怎么处理自己事务和调用方法事务之间的关系。
|
|
|
|
|
|
其中 propagation 有7种配置:REQUIRED、SUPPORTS、MANDATORY、REQUIRES\_NEW、NOT\_SUPPORTED、NEVER、NESTED。默认是 REQUIRED,它的含义是:如果本来有事务,则加入该事务,如果没有事务,则创建新的事务。
|
|
|
|
|
|
结合我们的伪代码示例,因为在 saveStudent() 上声明了一个外部的事务,就已经存在一个事务了,在propagation值为默认的REQUIRED的情况下, regCourse() 就会加入到已有的事务中,两个方法共用一个事务。
|
|
|
|
|
|
我们再来看下 Spring 事务处理的核心,其关键实现参考TransactionAspectSupport.invokeWithinTransaction():
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
protected Object invokeWithinTransaction(Method method, @Nullable Class<?> targetClass,
|
|
|
final InvocationCallback invocation) throws Throwable {
|
|
|
|
|
|
TransactionAttributeSource tas = getTransactionAttributeSource();
|
|
|
final TransactionAttribute txAttr = (tas != null ? tas.getTransactionAttribute(method, targetClass) : null);
|
|
|
final PlatformTransactionManager tm = determineTransactionManager(txAttr);
|
|
|
final String joinpointIdentification = methodIdentification(method, targetClass, txAttr);
|
|
|
if (txAttr == null || !(tm instanceof CallbackPreferringPlatformTransactionManager)) {
|
|
|
// 是否需要创建一个事务
|
|
|
TransactionInfo txInfo = createTransactionIfNecessary(tm, txAttr, joinpointIdentification);
|
|
|
Object retVal = null;
|
|
|
try {
|
|
|
// 调用具体的业务方法
|
|
|
retVal = invocation.proceedWithInvocation();
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
catch (Throwable ex) {
|
|
|
// 当发生异常时进行处理
|
|
|
completeTransactionAfterThrowing(txInfo, ex);
|
|
|
throw ex;
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
finally {
|
|
|
cleanupTransactionInfo(txInfo);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
// 正常返回时提交事务
|
|
|
commitTransactionAfterReturning(txInfo);
|
|
|
return retVal;
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
//......省略非关键代码.....
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
整个方法完成了事务的一整套处理逻辑,如下:
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. 检查是否需要创建事务;
|
|
|
2. 调用具体的业务方法进行处理;
|
|
|
3. 提交事务;
|
|
|
4. 处理异常。
|
|
|
|
|
|
这里要格外注意的是,当前案例是两个事务嵌套的场景,外层事务 doSaveStudent()和内层事务 regCourse(),每个事务都会调用到这个方法。所以,这个方法会被调用两次。下面我们来具体来看下内层事务对异常的处理。
|
|
|
|
|
|
当捕获了异常,会调用TransactionAspectSupport.completeTransactionAfterThrowing() 进行异常处理:
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
protected void completeTransactionAfterThrowing(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo, Throwable ex) {
|
|
|
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) {
|
|
|
if (txInfo.transactionAttribute != null && txInfo.transactionAttribute.rollbackOn(ex)) {
|
|
|
try {
|
|
|
txInfo.getTransactionManager().rollback(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
catch (TransactionSystemException ex2) {
|
|
|
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
|
|
|
ex2.initApplicationException(ex);
|
|
|
throw ex2;
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
catch (RuntimeException | Error ex2) {
|
|
|
logger.error("Application exception overridden by rollback exception", ex);
|
|
|
throw ex2;
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
//......省略非关键代码.....
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
在这个方法里,我们对异常类型做了一些检查,当符合声明中的定义后,执行了具体的 rollback 操作,这个操作是通过 TransactionManager.rollback() 完成的:
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
public final void rollback(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {
|
|
|
if (status.isCompleted()) {
|
|
|
throw new IllegalTransactionStateException(
|
|
|
"Transaction is already completed - do not call commit or rollback more than once per transaction");
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
DefaultTransactionStatus defStatus = (DefaultTransactionStatus) status;
|
|
|
processRollback(defStatus, false);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
而 rollback() 是在 AbstractPlatformTransactionManager 中实现的,继续调用了 processRollback():
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
private void processRollback(DefaultTransactionStatus status, boolean unexpected) {
|
|
|
try {
|
|
|
boolean unexpectedRollback = unexpected;
|
|
|
|
|
|
if (status.hasSavepoint()) {
|
|
|
// 有保存点
|
|
|
status.rollbackToHeldSavepoint();
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
else if (status.isNewTransaction()) {
|
|
|
// 是否为一个新的事务
|
|
|
doRollback(status);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
else {
|
|
|
// 处于一个更大的事务中
|
|
|
if (status.hasTransaction()) {
|
|
|
// 分支1
|
|
|
if (status.isLocalRollbackOnly() || isGlobalRollbackOnParticipationFailure()) {
|
|
|
doSetRollbackOnly(status);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
if (!isFailEarlyOnGlobalRollbackOnly()) {
|
|
|
unexpectedRollback = false;
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
// 省略非关键代码
|
|
|
if (unexpectedRollback) {
|
|
|
throw new UnexpectedRollbackException(
|
|
|
"Transaction rolled back because it has been marked as rollback-only");
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
finally {
|
|
|
cleanupAfterCompletion(status);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
这个方法里区分了三种不同类型的情况:
|
|
|
|
|
|
1. 是否有保存点;
|
|
|
2. 是否为一个新的事务;
|
|
|
3. 是否处于一个更大的事务中。
|
|
|
|
|
|
在这里,因为我们用的是默认的传播类型REQUIRED,嵌套的事务并没有开启一个新的事务,所以在这种情况下,当前事务是处于一个更大的事务中,所以会走到情况3分支1的代码块下。
|
|
|
|
|
|
这里有两个判断条件来确定是否设置为仅回滚:
|
|
|
if (status.isLocalRollbackOnly() || isGlobalRollbackOnParticipationFailure())
|
|
|
|
|
|
满足任何一个,都会执行 doSetRollbackOnly() 操作。isLocalRollbackOnly 在当前的情况下是 false,所以是否分设置为仅回滚就由 isGlobalRollbackOnParticipationFailure() 这个方法来决定了,其默认值为 true, 即是否回滚交由外层事务统一决定 。
|
|
|
|
|
|
显然这里的条件得到了满足,从而执行 doSetRollbackOnly:
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
protected void doSetRollbackOnly(DefaultTransactionStatus status) {
|
|
|
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) status.getTransaction();
|
|
|
txObject.setRollbackOnly();
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
以及最终调用到的**DataSourceTransactionObject中的setRollbackOnly():**
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
public void setRollbackOnly() {
|
|
|
getConnectionHolder().setRollbackOnly();
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
到这一步,内层事务的操作基本执行完毕,它处理了异常,并最终调用到了**DataSourceTransactionObject中的setRollbackOnly()**。
|
|
|
|
|
|
接下来,我们来看外层事务。因为在外层事务中,我们自己的代码捕获了内层抛出来的异常,所以这个异常不会继续往上抛,最后的事务会在 TransactionAspectSupport.invokeWithinTransaction() 中的 commitTransactionAfterReturning() 中进行处理:
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
protected void commitTransactionAfterReturning(@Nullable TransactionInfo txInfo) {
|
|
|
if (txInfo != null && txInfo.getTransactionStatus() != null) { txInfo.getTransactionManager().commit(txInfo.getTransactionStatus());
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
在这个方法里我们执行了 commit 操作,代码如下:
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
public final void commit(TransactionStatus status) throws TransactionException {
|
|
|
//......省略非关键代码.....
|
|
|
if (!shouldCommitOnGlobalRollbackOnly() && defStatus.isGlobalRollbackOnly()) {
|
|
|
processRollback(defStatus, true);
|
|
|
return;
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
processCommit(defStatus);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
在 AbstractPlatformTransactionManager.commit()中,当满足了 shouldCommitOnGlobalRollbackOnly() 和 defStatus.isGlobalRollbackOnly(),就会回滚,否则会继续提交事务。其中shouldCommitOnGlobalRollbackOnly()的作用为,如果发现了事务被标记了全局回滚,并且在发生了全局回滚的情况下,判断是否应该提交事务,这个方法的默认实现是返回了 false,这里我们不需要关注它,继续查看isGlobalRollbackOnly()的实现:
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
public boolean isGlobalRollbackOnly() {
|
|
|
return ((this.transaction instanceof SmartTransactionObject) &&
|
|
|
((SmartTransactionObject) this.transaction).isRollbackOnly());
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
这个方法最终进入了**DataSourceTransactionObject类中的isRollbackOnly():**
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
public boolean isRollbackOnly() {
|
|
|
return getConnectionHolder().isRollbackOnly();
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
现在让我们再次回顾一下之前的内部事务处理结果,其最终调用到的是**DataSourceTransactionObject中的setRollbackOnly():**
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
public void setRollbackOnly() {
|
|
|
getConnectionHolder().setRollbackOnly();
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
isRollbackOnly()和setRollbackOnly()这两个方法的执行本质都是对ConnectionHolder中rollbackOnly属性标志位的存取,而ConnectionHolder则存在于DefaultTransactionStatus类实例的transaction属性之中。
|
|
|
|
|
|
至此,答案基本浮出水面了,我们把整个逻辑串在一起就是:外层事务是否回滚的关键,最终取决于**DataSourceTransactionObject类中的isRollbackOnly(),而该方法的返回值,正是我们在内层异常的时候设置的**。
|
|
|
|
|
|
所以最终外层事务也被回滚了,从而在控制台中打印出异常信息:"Transaction rolled back because it has been marked as rollback-only"。
|
|
|
|
|
|
所以到这里,问题也就清楚了,Spring默认的事务传播属性为REQUIRED,如我们之前介绍的,它的含义是:如果本来有事务,则加入该事务,如果没有事务,则创建新的事务,因而内外两层事务都处于同一个事务中。所以,当我们在 regCourse()中抛出异常,并触发了回滚操作时,这个回滚会进一步传播,从而把 saveStudent() 也回滚了。最终导致整个事务都被回滚了。
|
|
|
|
|
|
### 问题修正
|
|
|
|
|
|
从上述案例解析中,我们了解到,Spring 在处理事务过程中,有个默认的传播属性 REQUIRED,在整个事务的调用链上,任何一个环节抛出的异常都会导致全局回滚。
|
|
|
|
|
|
知道了这个结论,修改方法也就很简单了,我们只需要对传播属性进行修改,把类型改成 REQUIRES\_NEW 就可以了。于是这部分代码就修改成这样:
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class, propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
|
|
|
public void regCourse(int studentId) throws Exception {
|
|
|
studentCourseMapper.saveStudentCourse(studentId, 1);
|
|
|
courseMapper.addCourseNumber(1);
|
|
|
throw new Exception("注册失败");
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
运行一下看看:
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
java.lang.Exception: 注册失败
|
|
|
at com.spring.puzzle.others.transaction.example3.CourseService.regCourse(CourseService.java:22)
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
异常正常抛出,注册课程部分的数据没有保存,但是学生还是正常注册成功。这意味着此时Spring 只对注册课程这部分的数据进行了回滚,并没有传播到上一级。
|
|
|
|
|
|
这里我简单解释下这个过程:
|
|
|
|
|
|
* 当子事务声明为 Propagation.REQUIRES\_NEW 时,在 TransactionAspectSupport.invokeWithinTransaction() 中调用 createTransactionIfNecessary() 就会创建一个新的事务,独立于外层事务。
|
|
|
* 而在 AbstractPlatformTransactionManager.processRollback() 进行 rollback 处理时,因为 status.isNewTransaction() 会因为它处于一个新的事务中而返回 true,所以它走入到了另一个分支,执行了 doRollback() 操作,让这个子事务单独回滚,不会影响到主事务。
|
|
|
|
|
|
至此,这个问题得到了很好的解决。
|
|
|
|
|
|
## 案例 2:多数据源间切换之谜
|
|
|
|
|
|
在前面的案例中,我们完成了学生注册功能和课程注册功能。假设新需求又来了,每个学生注册的时候,需要给他们发一张校园卡,并给校园卡里充入 50 元钱。但是这个校园卡管理系统是一个第三方系统,使用的是另一套数据库,这样我们就需要在一个事务中同时操作两个数据库。
|
|
|
|
|
|
第三方的 Card 表如下:
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
CREATE TABLE `card` (
|
|
|
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
|
|
|
`student_id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
|
|
|
`balance` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
|
|
|
PRIMARY KEY (`id`)
|
|
|
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8;
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
对应的 Card 对象如下:
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
public class Card {
|
|
|
private Integer id;
|
|
|
private Integer studentId;
|
|
|
private Integer balance;
|
|
|
//省略 Get/Set 方法
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
对应的 Mapper 接口如下,里面包含了一个 saveCard 的 insert 语句,用于创建一条校园卡记录:
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
@Mapper
|
|
|
public interface CardMapper {
|
|
|
@Insert("INSERT INTO `card`(`student_id`, `balance`) VALUES (#{studentId}, #{balance})")
|
|
|
@Options(useGeneratedKeys = true, keyProperty = "id")
|
|
|
int saveCard(Card card);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
Card 的业务类如下,里面实现了卡与学生 ID 关联,以及充入 50 元的操作:
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
@Service
|
|
|
public class CardService {
|
|
|
@Autowired
|
|
|
private CardMapper cardMapper;
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Transactional
|
|
|
public void createCard(int studentId) throws Exception {
|
|
|
Card card = new Card();
|
|
|
card.setStudentId(studentId);
|
|
|
card.setBalance(50);
|
|
|
cardMapper.saveCard(card);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
### 案例解析
|
|
|
|
|
|
这是一个相对常见的需求,学生注册和发卡都要在一个事务里完成,但是我们都默认只会连一个数据源,之前我们一直连的都是学生信息这个数据源,在这里,我们还需要对校园卡的数据源进行操作。于是,我们需要在一个事务里完成对两个数据源的操作,该如何实现这样的功能呢?
|
|
|
|
|
|
我们继续从 Spring 的源码中寻找答案。在 Spring 里有这样一个抽象类 AbstractRoutingDataSource,这个类相当于 DataSource 的路由中介,在运行时根据某种 key 值来动态切换到所需的 DataSource 上。通过实现这个类就可以实现我们期望的动态数据源切换。
|
|
|
|
|
|
这里强调一下,这个类里有这么几个关键属性:
|
|
|
|
|
|
* targetDataSources 保存了 key 和数据库连接的映射关系;
|
|
|
* defaultTargetDataSource 标识默认的连接;
|
|
|
* resolvedDataSources 存储数据库标识和数据源的映射关系。
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
public abstract class AbstractRoutingDataSource extends AbstractDataSource implements InitializingBean {
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Nullable
|
|
|
private Map<Object, Object> targetDataSources;
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Nullable
|
|
|
private Object defaultTargetDataSource;
|
|
|
|
|
|
private boolean lenientFallback = true;
|
|
|
|
|
|
private DataSourceLookup dataSourceLookup = new JndiDataSourceLookup();
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Nullable
|
|
|
private Map<Object, DataSource> resolvedDataSources;
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Nullable
|
|
|
private DataSource resolvedDefaultDataSource;
|
|
|
|
|
|
//省略非关键代码
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
AbstractRoutingDataSource 实现了 InitializingBean 接口,并覆写了 afterPropertiesSet()。该方法会在初始化 Bean 的时候执行,将多个 DataSource 初始化到 resolvedDataSources。这里的 targetDataSources 属性存储了将要切换的多数据源 Bean 信息。
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
@Override
|
|
|
public void afterPropertiesSet() {
|
|
|
if (this.targetDataSources == null) {
|
|
|
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Property 'targetDataSources' is required");
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
this.resolvedDataSources = new HashMap<>(this.targetDataSources.size());
|
|
|
this.targetDataSources.forEach((key, value) -> {
|
|
|
Object lookupKey = resolveSpecifiedLookupKey(key);
|
|
|
DataSource dataSource = resolveSpecifiedDataSource(value);
|
|
|
this.resolvedDataSources.put(lookupKey, dataSource);
|
|
|
});
|
|
|
if (this.defaultTargetDataSource != null) {
|
|
|
this.resolvedDefaultDataSource = resolveSpecifiedDataSource(this.defaultTargetDataSource);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
获取数据库连接的是 getConnection(),它调用了 determineTargetDataSource()来创建连接:
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
@Override
|
|
|
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
|
|
|
return determineTargetDataSource().getConnection();
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Override
|
|
|
public Connection getConnection(String username, String password) throws SQLException {
|
|
|
return determineTargetDataSource().getConnection(username, password);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
determineTargetDataSource()是整个部分的核心,它的作用就是动态切换数据源。有多少个数据源,就存多少个数据源在 targetDataSources 中。
|
|
|
|
|
|
targetDataSources 是一个 Map 类型的属性,key 表示每个数据源的名字,value 对应的是每个数据源 DataSource。
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
protected DataSource determineTargetDataSource() {
|
|
|
Assert.notNull(this.resolvedDataSources, "DataSource router not initialized");
|
|
|
Object lookupKey = determineCurrentLookupKey();
|
|
|
DataSource dataSource = this.resolvedDataSources.get(lookupKey);
|
|
|
if (dataSource == null && (this.lenientFallback || lookupKey == null)) {
|
|
|
dataSource = this.resolvedDefaultDataSource;
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
if (dataSource == null) {
|
|
|
throw new IllegalStateException("Cannot determine target DataSource for lookup key [" + lookupKey + "]");
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
return dataSource;
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
而选择哪个数据源又是由 determineCurrentLookupKey()来决定的,此方法是抽象方法,需要我们继承 AbstractRoutingDataSource 抽象类来重写此方法。该方法返回一个 key,该 key 是 Bean 中的 beanName,并赋值给 lookupKey,由此 key 可以通过 resolvedDataSources 属性的键来获取对应的 DataSource 值,从而达到数据源切换的效果。
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
protected abstract Object determineCurrentLookupKey();
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
这样看来,这个方法的实现就得由我们完成了。接下来我们将会完成一系列相关的代码,解决这个问题。
|
|
|
|
|
|
### 问题修正
|
|
|
|
|
|
首先,我们创建一个 MyDataSource 类,继承了 AbstractRoutingDataSource,并覆写了 determineCurrentLookupKey():
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
public class MyDataSource extends AbstractRoutingDataSource {
|
|
|
private static final ThreadLocal<String> key = new ThreadLocal<String>();
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Override
|
|
|
protected Object determineCurrentLookupKey() {
|
|
|
return key.get();
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
public static void setDataSource(String dataSource) {
|
|
|
key.set(dataSource);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
public static String getDatasource() {
|
|
|
return key.get();
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
public static void clearDataSource() {
|
|
|
key.remove();
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
其次,我们需要修改 JdbcConfig。这里我新写了一个 dataSource,将原来的 dataSource 改成 dataSourceCore,再将新定义的 dataSourceCore 和 dataSourceCard 放进一个 Map,对应的 key 分别是 core 和 card,并把 Map 赋值给 setTargetDataSources
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
public class JdbcConfig {
|
|
|
//省略非关键代码
|
|
|
@Value("${card.driver}")
|
|
|
private String cardDriver;
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Value("${card.url}")
|
|
|
private String cardUrl;
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Value("${card.username}")
|
|
|
private String cardUsername;
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Value("${card.password}")
|
|
|
private String cardPassword;
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Autowired
|
|
|
@Qualifier("dataSourceCard")
|
|
|
private DataSource dataSourceCard;
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Autowired
|
|
|
@Qualifier("dataSourceCore")
|
|
|
private DataSource dataSourceCore;
|
|
|
|
|
|
//省略非关键代码
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Bean(name = "dataSourceCore")
|
|
|
public DataSource createCoreDataSource() {
|
|
|
DriverManagerDataSource ds = new DriverManagerDataSource();
|
|
|
ds.setDriverClassName(driver);
|
|
|
ds.setUrl(url);
|
|
|
ds.setUsername(username);
|
|
|
ds.setPassword(password);
|
|
|
return ds;
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Bean(name = "dataSourceCard")
|
|
|
public DataSource createCardDataSource() {
|
|
|
DriverManagerDataSource ds = new DriverManagerDataSource();
|
|
|
ds.setDriverClassName(cardDriver);
|
|
|
ds.setUrl(cardUrl);
|
|
|
ds.setUsername(cardUsername);
|
|
|
ds.setPassword(cardPassword);
|
|
|
return ds;
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Bean(name = "dataSource")
|
|
|
public MyDataSource createDataSource() {
|
|
|
MyDataSource myDataSource = new MyDataSource();
|
|
|
Map<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
|
|
|
map.put("core", dataSourceCore);
|
|
|
map.put("card", dataSourceCard);
|
|
|
myDataSource.setTargetDataSources(map);
|
|
|
myDataSource.setDefaultTargetDataSource(dataSourceCore);
|
|
|
return myDataSource;
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
//省略非关键代码
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
最后还剩下一个问题,setDataSource 这个方法什么时候执行呢?
|
|
|
|
|
|
我们可以用 Spring AOP 来设置,把配置的数据源类型都设置成注解标签, Service层中在切换数据源的方法上加上注解标签,就会调用相应的方法切换数据源。
|
|
|
|
|
|
我们定义了一个新的注解 @DataSource,可以直接加在 Service()上,实现数据库切换:
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
@Documented
|
|
|
@Target({ElementType.TYPE, ElementType.METHOD})
|
|
|
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
|
|
|
public @interface DataSource {
|
|
|
String value();
|
|
|
|
|
|
String core = "core";
|
|
|
|
|
|
String card = "card";
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
声明方法如下:
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
@DataSource(DataSource.card)
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
另外,我们还需要写一个 Spring AOP 来对相应的服务方法进行拦截,完成数据源的切换操作。特别要注意的是,这里要加上一个 @Order(1) 标记它的初始化顺序。这个 Order 值一定要比事务的 AOP 切面的值小,这样可以获得更高的优先级,否则自动切换数据源将会失效。
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
@Aspect
|
|
|
@Service
|
|
|
@Order(1)
|
|
|
public class DataSourceSwitch {
|
|
|
@Around("execution(* com.spring.puzzle.others.transaction.example3.CardService.*(..))")
|
|
|
public void around(ProceedingJoinPoint point) throws Throwable {
|
|
|
Signature signature = point.getSignature();
|
|
|
MethodSignature methodSignature = (MethodSignature) signature;
|
|
|
Method method = methodSignature.getMethod();
|
|
|
if (method.isAnnotationPresent(DataSource.class)) {
|
|
|
DataSource dataSource = method.getAnnotation(DataSource.class);
|
|
|
MyDataSource.setDataSource(dataSource.value());
|
|
|
System.out.println("数据源切换至:" + MyDataSource.getDatasource());
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
point.proceed();
|
|
|
MyDataSource.clearDataSource();
|
|
|
System.out.println("数据源已移除!");
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
最后,我们实现了 Card 的发卡逻辑,在方法前声明了切换数据库:
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
@Service
|
|
|
public class CardService {
|
|
|
@Autowired
|
|
|
private CardMapper cardMapper;
|
|
|
|
|
|
@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES_NEW)
|
|
|
@DataSource(DataSource.card)
|
|
|
public void createCard(int studentId) throws Exception {
|
|
|
Card card = new Card();
|
|
|
card.setStudentId(studentId);
|
|
|
card.setBalance(50);
|
|
|
cardMapper.saveCard(card);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
并在 saveStudent() 里调用了发卡逻辑:
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
|
|
|
public void saveStudent(String realname) throws Exception {
|
|
|
Student student = new Student();
|
|
|
student.setRealname(realname);
|
|
|
studentService.doSaveStudent(student);
|
|
|
try {
|
|
|
courseService.regCourse(student.getId());
|
|
|
cardService.createCard(student.getId());
|
|
|
} catch (Exception e) {
|
|
|
e.printStackTrace();
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
执行一下,一切正常,两个库的数据都可以正常保存了。
|
|
|
|
|
|
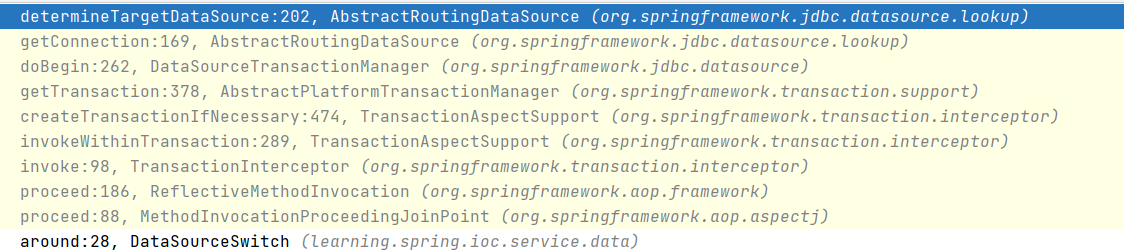
最后我们来看一下整个过程的调用栈,重新过一遍流程(这里我略去了不重要的部分)。
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
在创建了事务以后,会通过 DataSourceTransactionManager.doBegin()获取相应的数据库连接:
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
protected void doBegin(Object transaction, TransactionDefinition definition) {
|
|
|
DataSourceTransactionObject txObject = (DataSourceTransactionObject) transaction;
|
|
|
Connection con = null;
|
|
|
|
|
|
try {
|
|
|
if (!txObject.hasConnectionHolder() ||
|
|
|
txObject.getConnectionHolder().isSynchronizedWithTransaction()) {
|
|
|
Connection newCon = obtainDataSource().getConnection();
|
|
|
txObject.setConnectionHolder(new ConnectionHolder(newCon), true);
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
//省略非关键代码
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
这里的 obtainDataSource().getConnection() 调用到了 AbstractRoutingDataSource.getConnection(),这就与我们实现的功能顺利会师了。
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
public Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
|
|
|
return determineTargetDataSource().getConnection();
|
|
|
}
|
|
|
|
|
|
```
|
|
|
|
|
|
## 重点回顾
|
|
|
|
|
|
通过以上两个案例,相信你对 Spring 的事务机制已经有了深刻的认识,最后总结下重点:
|
|
|
|
|
|
* Spring 在事务处理中有一个很重要的属性 Propagation,主要用来配置当前需要执行的方法如何使用事务,以及与其它事务之间的关系。
|
|
|
* Spring 默认的传播属性是 REQUIRED,在有事务状态下执行,如果当前没有事务,则创建新的事务;
|
|
|
* Spring 事务是可以对多个数据源生效,它提供了一个抽象类 AbstractRoutingDataSource,通过实现这个抽象类,我们可以实现自定义的数据库切换。
|
|
|
|
|
|
## 思考题
|
|
|
|
|
|
结合案例2,请你思考这样一个问题:在这个案例中,我们在 CardService类方法上声明了这样的事务传播属性,@Transactional(propagation = Propagation.REQUIRES\_NEW),如果使用 Spring 的默认声明行不行,为什么?
|
|
|
|
|
|
期待你的思考,我们留言区见!
|
|
|
|