580 lines
20 KiB
Markdown
580 lines
20 KiB
Markdown
# 57 | Namespace技术:内部创业公司应该独立运营
|
||
|
||
上一节我们讲了Docker的基本原理,今天我们来看一下,“看起来隔离的”技术namespace在内核里面是如何工作的。
|
||
|
||
既然容器是一种类似公司内部创业的技术,我们可以设想一下,如果一个创新项目要独立运营,应该成立哪些看起来独立的组织和部门呢?
|
||
|
||
首先是**用户管理**,咱们这个小分队应该有自己独立的用户和组管理体系,公司里面并不是任何人都知道我们在做什么。
|
||
|
||
其次是**项目管理**,咱们应该有自己独立的项目管理体系,不能按照大公司的来。
|
||
|
||
然后是**档案管理**,咱们这个创新项目的资料一定要保密,要不然创意让人家偷走了可不好。
|
||
|
||
最后就是**合作部**,咱们这个小分队还是要和公司其他部门或者其他公司合作的,所以需要一个外向的人来干这件事情。
|
||
|
||
对应到容器技术,为了隔离不同类型的资源,Linux内核里面实现了以下几种不同类型的namespace。
|
||
|
||
* UTS,对应的宏为CLONE\_NEWUTS,表示不同的namespace可以配置不同的hostname。
|
||
* User,对应的宏为CLONE\_NEWUSER,表示不同的namespace可以配置不同的用户和组。
|
||
* Mount,对应的宏为CLONE\_NEWNS,表示不同的namespace的文件系统挂载点是隔离的
|
||
* PID,对应的宏为CLONE\_NEWPID,表示不同的namespace有完全独立的pid,也即一个namespace的进程和另一个namespace的进程,pid可以是一样的,但是代表不同的进程。
|
||
* Network,对应的宏为CLONE\_NEWNET,表示不同的namespace有独立的网络协议栈。
|
||
|
||
还记得咱们启动的那个容器吗?
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# docker ps
|
||
CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES
|
||
f604f0e34bc2 testnginx:1 "/bin/sh -c 'nginx -…" 17 hours ago Up 17 hours 0.0.0.0:8081->80/tcp youthful_torvalds
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
我们可以看这个容器对应的entrypoint的pid。通过docker inspect命令,可以看到,进程号为58212。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
[root@deployer ~]# docker inspect f604f0e34bc2
|
||
[
|
||
{
|
||
"Id": "f604f0e34bc263bc32ba683d97a1db2a65de42ab052da16df3c7811ad07f0dc3",
|
||
"Created": "2019-07-15T17:43:44.158300531Z",
|
||
"Path": "/bin/sh",
|
||
"Args": [
|
||
"-c",
|
||
"nginx -g \"daemon off;\""
|
||
],
|
||
"State": {
|
||
"Status": "running",
|
||
"Running": true,
|
||
"Pid": 58212,
|
||
"ExitCode": 0,
|
||
"StartedAt": "2019-07-15T17:43:44.651756682Z",
|
||
"FinishedAt": "0001-01-01T00:00:00Z"
|
||
},
|
||
......
|
||
"Name": "/youthful_torvalds",
|
||
"RestartCount": 0,
|
||
"Driver": "overlay2",
|
||
"Platform": "linux",
|
||
"HostConfig": {
|
||
"NetworkMode": "default",
|
||
"PortBindings": {
|
||
"80/tcp": [
|
||
{
|
||
"HostIp": "",
|
||
"HostPort": "8081"
|
||
}
|
||
]
|
||
},
|
||
......
|
||
},
|
||
"Config": {
|
||
"Hostname": "f604f0e34bc2",
|
||
"ExposedPorts": {
|
||
"80/tcp": {}
|
||
},
|
||
"Image": "testnginx:1",
|
||
"Entrypoint": [
|
||
"/bin/sh",
|
||
"-c",
|
||
"nginx -g \"daemon off;\""
|
||
],
|
||
},
|
||
"NetworkSettings": {
|
||
"Bridge": "",
|
||
"SandboxID": "7fd3eb469578903b66687090e512958658ae28d17bce1a7cee2da3148d1dfad4",
|
||
"Ports": {
|
||
"80/tcp": [
|
||
{
|
||
"HostIp": "0.0.0.0",
|
||
"HostPort": "8081"
|
||
}
|
||
]
|
||
},
|
||
"Gateway": "172.17.0.1",
|
||
"IPAddress": "172.17.0.3",
|
||
"IPPrefixLen": 16,
|
||
"MacAddress": "02:42:ac:11:00:03",
|
||
"Networks": {
|
||
"bridge": {
|
||
"NetworkID": "c8eef1603afb399bf17af154be202fd1e543d3772cc83ef4a1ca3f97b8bd6eda",
|
||
"EndpointID": "8d9bb18ca57889112e758ede193d2cfb45cbf794c9d952819763c08f8545da46",
|
||
"Gateway": "172.17.0.1",
|
||
"IPAddress": "172.17.0.3",
|
||
"IPPrefixLen": 16,
|
||
"MacAddress": "02:42:ac:11:00:03",
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
}
|
||
]
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
如果我们用ps查看机器上的nginx进程,可以看到master和worker,worker的父进程是master。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# ps -ef |grep nginx
|
||
root 58212 58195 0 01:43 ? 00:00:00 /bin/sh -c nginx -g "daemon off;"
|
||
root 58244 58212 0 01:43 ? 00:00:00 nginx: master process nginx -g daemon off;
|
||
33 58250 58244 0 01:43 ? 00:00:00 nginx: worker process
|
||
33 58251 58244 0 01:43 ? 00:00:05 nginx: worker process
|
||
33 58252 58244 0 01:43 ? 00:00:05 nginx: worker process
|
||
33 58253 58244 0 01:43 ? 00:00:05 nginx: worker process
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
在/proc/pid/ns里面,我们能够看到这个进程所属于的6种namespace。我们拿出两个进程来,应该可以看出来,它们属于同一个namespace。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# ls -l /proc/58212/ns
|
||
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jul 16 19:19 ipc -> ipc:[4026532278]
|
||
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jul 16 19:19 mnt -> mnt:[4026532276]
|
||
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jul 16 01:43 net -> net:[4026532281]
|
||
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jul 16 19:19 pid -> pid:[4026532279]
|
||
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jul 16 19:19 user -> user:[4026531837]
|
||
lrwxrwxrwx 1 root root 0 Jul 16 19:19 uts -> uts:[4026532277]
|
||
|
||
# ls -l /proc/58253/ns
|
||
lrwxrwxrwx 1 33 tape 0 Jul 16 19:20 ipc -> ipc:[4026532278]
|
||
lrwxrwxrwx 1 33 tape 0 Jul 16 19:20 mnt -> mnt:[4026532276]
|
||
lrwxrwxrwx 1 33 tape 0 Jul 16 19:20 net -> net:[4026532281]
|
||
lrwxrwxrwx 1 33 tape 0 Jul 16 19:20 pid -> pid:[4026532279]
|
||
lrwxrwxrwx 1 33 tape 0 Jul 16 19:20 user -> user:[4026531837]
|
||
lrwxrwxrwx 1 33 tape 0 Jul 16 19:20 uts -> uts:[4026532277]
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
接下来,我们来看,如何操作namespace。这里我们重点关注pid和network。
|
||
|
||
操作namespace的常用指令**nsenter**,可以用来运行一个进程,进入指定的namespace。例如,通过下面的命令,我们可以运行/bin/bash,并且进入nginx所在容器的namespace。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# nsenter --target 58212 --mount --uts --ipc --net --pid -- env --ignore-environment -- /bin/bash
|
||
|
||
root@f604f0e34bc2:/# ip addr
|
||
1: lo: <LOOPBACK,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 65536 qdisc noqueue state UNKNOWN group default qlen 1000
|
||
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
|
||
inet 127.0.0.1/8 scope host lo
|
||
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
|
||
23: eth0@if24: <BROADCAST,MULTICAST,UP,LOWER_UP> mtu 1500 qdisc noqueue state UP group default
|
||
link/ether 02:42:ac:11:00:03 brd ff:ff:ff:ff:ff:ff
|
||
inet 172.17.0.3/16 brd 172.17.255.255 scope global eth0
|
||
valid_lft forever preferred_lft forever
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
另一个命令是**unshare**,它会离开当前的namespace,创建且加入新的namespace,然后执行参数中指定的命令。
|
||
|
||
例如,运行下面这行命令之后,pid和net都进入了新的namespace。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
unshare --mount --ipc --pid --net --mount-proc=/proc --fork /bin/bash
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
如果从shell上运行上面这行命令的话,好像没有什么变化,但是因为pid和net都进入了新的namespace,所以我们查看进程列表和ip地址的时候应该会发现有所不同。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# ip addr
|
||
1: lo: <LOOPBACK> mtu 65536 qdisc noop state DOWN group default qlen 1000
|
||
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
|
||
|
||
# ps aux
|
||
USER PID %CPU %MEM VSZ RSS TTY STAT START TIME COMMAND
|
||
root 1 0.0 0.0 115568 2136 pts/0 S 22:55 0:00 /bin/bash
|
||
root 13 0.0 0.0 155360 1872 pts/0 R+ 22:55 0:00 ps aux
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
果真,我们看不到宿主机上的IP地址和网卡了,也看不到宿主机上的所有进程了。
|
||
|
||
另外,我们还可以通过函数操作namespace。
|
||
|
||
第一个函数是**clone**,也就是创建一个新的进程,并把它放到新的namespace中。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
int clone(int (*fn)(void *), void *child_stack, int flags, void *arg);
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
clone函数我们原来介绍过。这里面有一个参数flags,原来我们没有注意它。其实它可以设置为CLONE\_NEWUTS、CLONE\_NEWUSER、CLONE\_NEWNS、CLONE\_NEWPID。CLONE\_NEWNET会将clone出来的新进程放到新的namespace中。
|
||
|
||
第二个函数是**setns**,用于将当前进程加入到已有的namespace中。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
int setns(int fd, int nstype);
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
其中,fd指向/proc/\[pid\]/ns/目录里相应namespace对应的文件,表示要加入哪个namespace。nstype用来指定namespace的类型,可以设置为CLONE\_NEWUTS、CLONE\_NEWUSER、CLONE\_NEWNS、CLONE\_NEWPID和CLONE\_NEWNET。
|
||
|
||
第三个函数是**unshare**,它可以使当前进程退出当前的namespace,并加入到新创建的namespace。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
int unshare(int flags);
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
其中,flags用于指定一个或者多个上面的CLONE\_NEWUTS、CLONE\_NEWUSER、CLONE\_NEWNS、CLONE\_NEWPID和CLONE\_NEWNET。
|
||
|
||
clone和unshare的区别是,unshare是使当前进程加入新的namespace;clone是创建一个新的子进程,然后让子进程加入新的namespace,而当前进程保持不变。
|
||
|
||
这里我们尝试一下,通过clone函数来进入一个namespace。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
#define _GNU_SOURCE
|
||
#include <sys/wait.h>
|
||
#include <sys/utsname.h>
|
||
#include <sched.h>
|
||
#include <string.h>
|
||
#include <stdio.h>
|
||
#include <stdlib.h>
|
||
#include <unistd.h>
|
||
#define STACK_SIZE (1024 * 1024)
|
||
|
||
static int childFunc(void *arg)
|
||
{
|
||
printf("In child process.\n");
|
||
execlp("bash", "bash", (char *) NULL);
|
||
return 0;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
|
||
{
|
||
char *stack;
|
||
char *stackTop;
|
||
pid_t pid;
|
||
|
||
stack = malloc(STACK_SIZE);
|
||
if (stack == NULL)
|
||
{
|
||
perror("malloc");
|
||
exit(1);
|
||
}
|
||
stackTop = stack + STACK_SIZE;
|
||
|
||
pid = clone(childFunc, stackTop, CLONE_NEWNS|CLONE_NEWPID|CLONE_NEWNET|SIGCHLD, NULL);
|
||
if (pid == -1)
|
||
{
|
||
perror("clone");
|
||
exit(1);
|
||
}
|
||
printf("clone() returned %ld\n", (long) pid);
|
||
|
||
sleep(1);
|
||
|
||
if (waitpid(pid, NULL, 0) == -1)
|
||
{
|
||
perror("waitpid");
|
||
exit(1);
|
||
}
|
||
printf("child has terminated\n");
|
||
exit(0);
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
在上面的代码中,我们调用clone的时候,给的参数是CLONE\_NEWNS|CLONE\_NEWPID|CLONE\_NEWNET,也就是说,我们会进入一个新的pid、network,以及mount的namespace。
|
||
|
||
如果我们编译运行它,可以得到下面的结果。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
# echo $$
|
||
64267
|
||
|
||
# ps aux | grep bash | grep -v grep
|
||
root 64267 0.0 0.0 115572 2176 pts/0 Ss 16:53 0:00 -bash
|
||
|
||
# ./a.out
|
||
clone() returned 64360
|
||
In child process.
|
||
|
||
# echo $$
|
||
1
|
||
|
||
# ip addr
|
||
1: lo: <LOOPBACK> mtu 65536 qdisc noop state DOWN group default qlen 1000
|
||
link/loopback 00:00:00:00:00:00 brd 00:00:00:00:00:00
|
||
|
||
# exit
|
||
exit
|
||
child has terminated
|
||
|
||
# echo $$
|
||
64267
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
通过`echo $$`,我们可以得到当前bash的进程号。一旦运行了上面的程序,我们就会进入一个新的pid的namespace。
|
||
|
||
当我们再次`echo $$`的时候就会发现,当前bash的进程号变成了1。上面的程序运行了一个新的bash,它在一个独立的pid namespace里面,自己是1号进程。如果运行ip addr,可以看到,宿主机的网卡都找不到了,因为新的bash也在一个独立的network namespace里面,等退出了,再次echo $$的时候,就可以得到原来进程号。
|
||
|
||
clone系统调用我们在[进程的创建](https://time.geekbang.org/column/article/94064)那一节解析过,当时我们没有看关于namespace的代码,现在我们就来看一看,namespace在内核做了哪些事情。
|
||
|
||
在内核里面,clone会调用\_do\_fork->copy\_process->copy\_namespaces,也就是说,在创建子进程的时候,有一个机会可以复制和设置namespace。
|
||
|
||
namespace是在哪里定义的呢?在每一个进程的task\_struct里面,有一个指向namespace结构体的指针nsproxy。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
struct task_struct {
|
||
......
|
||
/* Namespaces: */
|
||
struct nsproxy *nsproxy;
|
||
......
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
/*
|
||
* A structure to contain pointers to all per-process
|
||
* namespaces - fs (mount), uts, network, sysvipc, etc.
|
||
*
|
||
* The pid namespace is an exception -- it's accessed using
|
||
* task_active_pid_ns. The pid namespace here is the
|
||
* namespace that children will use.
|
||
*/
|
||
struct nsproxy {
|
||
atomic_t count;
|
||
struct uts_namespace *uts_ns;
|
||
struct ipc_namespace *ipc_ns;
|
||
struct mnt_namespace *mnt_ns;
|
||
struct pid_namespace *pid_ns_for_children;
|
||
struct net *net_ns;
|
||
struct cgroup_namespace *cgroup_ns;
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
我们可以看到在struct nsproxy结构里面,有我们上面讲过的各种namespace。
|
||
|
||
在系统初始化的时候,有一个默认的init\_nsproxy。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
struct nsproxy init_nsproxy = {
|
||
.count = ATOMIC_INIT(1),
|
||
.uts_ns = &init_uts_ns,
|
||
#if defined(CONFIG_POSIX_MQUEUE) || defined(CONFIG_SYSVIPC)
|
||
.ipc_ns = &init_ipc_ns,
|
||
#endif
|
||
.mnt_ns = NULL,
|
||
.pid_ns_for_children = &init_pid_ns,
|
||
#ifdef CONFIG_NET
|
||
.net_ns = &init_net,
|
||
#endif
|
||
#ifdef CONFIG_CGROUPS
|
||
.cgroup_ns = &init_cgroup_ns,
|
||
#endif
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
下面,我们来看copy\_namespaces的实现。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
/*
|
||
* called from clone. This now handles copy for nsproxy and all
|
||
* namespaces therein.
|
||
*/
|
||
int copy_namespaces(unsigned long flags, struct task_struct *tsk)
|
||
{
|
||
struct nsproxy *old_ns = tsk->nsproxy;
|
||
struct user_namespace *user_ns = task_cred_xxx(tsk, user_ns);
|
||
struct nsproxy *new_ns;
|
||
|
||
if (likely(!(flags & (CLONE_NEWNS | CLONE_NEWUTS | CLONE_NEWIPC |
|
||
CLONE_NEWPID | CLONE_NEWNET |
|
||
CLONE_NEWCGROUP)))) {
|
||
get_nsproxy(old_ns);
|
||
return 0;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
if (!ns_capable(user_ns, CAP_SYS_ADMIN))
|
||
return -EPERM;
|
||
......
|
||
new_ns = create_new_namespaces(flags, tsk, user_ns, tsk->fs);
|
||
|
||
tsk->nsproxy = new_ns;
|
||
return 0;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
如果clone的参数里面没有CLONE\_NEWNS | CLONE\_NEWUTS | CLONE\_NEWIPC | CLONE\_NEWPID | CLONE\_NEWNET | CLONE\_NEWCGROUP,就返回原来的namespace,调用get\_nsproxy。
|
||
|
||
接着,我们调用create\_new\_namespaces。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
/*
|
||
* Create new nsproxy and all of its the associated namespaces.
|
||
* Return the newly created nsproxy. Do not attach this to the task,
|
||
* leave it to the caller to do proper locking and attach it to task.
|
||
*/
|
||
static struct nsproxy *create_new_namespaces(unsigned long flags,
|
||
struct task_struct *tsk, struct user_namespace *user_ns,
|
||
struct fs_struct *new_fs)
|
||
{
|
||
struct nsproxy *new_nsp;
|
||
|
||
new_nsp = create_nsproxy();
|
||
......
|
||
new_nsp->mnt_ns = copy_mnt_ns(flags, tsk->nsproxy->mnt_ns, user_ns, new_fs);
|
||
......
|
||
new_nsp->uts_ns = copy_utsname(flags, user_ns, tsk->nsproxy->uts_ns);
|
||
......
|
||
new_nsp->ipc_ns = copy_ipcs(flags, user_ns, tsk->nsproxy->ipc_ns);
|
||
......
|
||
new_nsp->pid_ns_for_children =
|
||
copy_pid_ns(flags, user_ns, tsk->nsproxy->pid_ns_for_children);
|
||
......
|
||
new_nsp->cgroup_ns = copy_cgroup_ns(flags, user_ns,
|
||
tsk->nsproxy->cgroup_ns);
|
||
......
|
||
new_nsp->net_ns = copy_net_ns(flags, user_ns, tsk->nsproxy->net_ns);
|
||
......
|
||
return new_nsp;
|
||
......
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
在create\_new\_namespaces中,我们可以看到对于各种namespace的复制。
|
||
|
||
我们来看copy\_pid\_ns对于pid namespace的复制。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
struct pid_namespace *copy_pid_ns(unsigned long flags,
|
||
struct user_namespace *user_ns, struct pid_namespace *old_ns)
|
||
{
|
||
if (!(flags & CLONE_NEWPID))
|
||
return get_pid_ns(old_ns);
|
||
if (task_active_pid_ns(current) != old_ns)
|
||
return ERR_PTR(-EINVAL);
|
||
return create_pid_namespace(user_ns, old_ns);
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
在copy\_pid\_ns中,如果没有设置CLONE\_NEWPID,则返回老的pid namespace;如果设置了,就调用create\_pid\_namespace,创建新的pid namespace.
|
||
|
||
我们再来看copy\_net\_ns对于network namespace的复制。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
struct net *copy_net_ns(unsigned long flags,
|
||
struct user_namespace *user_ns, struct net *old_net)
|
||
{
|
||
struct ucounts *ucounts;
|
||
struct net *net;
|
||
int rv;
|
||
|
||
if (!(flags & CLONE_NEWNET))
|
||
return get_net(old_net);
|
||
|
||
ucounts = inc_net_namespaces(user_ns);
|
||
......
|
||
net = net_alloc();
|
||
......
|
||
get_user_ns(user_ns);
|
||
net->ucounts = ucounts;
|
||
rv = setup_net(net, user_ns);
|
||
......
|
||
return net;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
在这里面,我们需要判断,如果flags中不包含CLONE\_NEWNET,也就是不会创建一个新的network namespace,则返回old\_net;否则需要新建一个network namespace。
|
||
|
||
然后,copy\_net\_ns会调用net = net\_alloc(),分配一个新的struct net结构,然后调用setup\_net对新分配的net结构进行初始化,之后调用list\_add\_tail\_rcu,将新建的network namespace,添加到全局的network namespace列表net\_namespace\_list中。
|
||
|
||
我们来看一下setup\_net的实现。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
/*
|
||
* setup_net runs the initializers for the network namespace object.
|
||
*/
|
||
static __net_init int setup_net(struct net *net, struct user_namespace *user_ns)
|
||
{
|
||
/* Must be called with net_mutex held */
|
||
const struct pernet_operations *ops, *saved_ops;
|
||
LIST_HEAD(net_exit_list);
|
||
|
||
atomic_set(&net->count, 1);
|
||
refcount_set(&net->passive, 1);
|
||
net->dev_base_seq = 1;
|
||
net->user_ns = user_ns;
|
||
idr_init(&net->netns_ids);
|
||
spin_lock_init(&net->nsid_lock);
|
||
|
||
list_for_each_entry(ops, &pernet_list, list) {
|
||
error = ops_init(ops, net);
|
||
......
|
||
}
|
||
......
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
在setup\_net中,这里面有一个循环list\_for\_each\_entry,对于pernet\_list的每一项struct pernet\_operations,运行ops\_init,也就是调用pernet\_operations的init函数。
|
||
|
||
这个pernet\_list是怎么来的呢?在网络设备初始化的时候,我们要调用net\_dev\_init函数,这里面有下面的代码。
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
register_pernet_device(&loopback_net_ops)
|
||
|
||
int register_pernet_device(struct pernet_operations *ops)
|
||
{
|
||
int error;
|
||
mutex_lock(&net_mutex);
|
||
error = register_pernet_operations(&pernet_list, ops);
|
||
if (!error && (first_device == &pernet_list))
|
||
first_device = &ops->list;
|
||
mutex_unlock(&net_mutex);
|
||
return error;
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
struct pernet_operations __net_initdata loopback_net_ops = {
|
||
.init = loopback_net_init,
|
||
};
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
register\_pernet\_device函数注册了一个loopback\_net\_ops,在这里面,把init函数设置为loopback\_net\_init.
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
static __net_init int loopback_net_init(struct net *net)
|
||
{
|
||
struct net_device *dev;
|
||
dev = alloc_netdev(0, "lo", NET_NAME_UNKNOWN, loopback_setup);
|
||
......
|
||
dev_net_set(dev, net);
|
||
err = register_netdev(dev);
|
||
......
|
||
net->loopback_dev = dev;
|
||
return 0;
|
||
......
|
||
}
|
||
|
||
```
|
||
|
||
在loopback\_net\_init函数中,我们会创建并且注册一个名字为"lo"的struct net\_device。注册完之后,在这个namespace里面就会出现一个这样的网络设备,称为loopback网络设备。
|
||
|
||
这就是为什么上面的实验中,创建出的新的network namespace里面有一个lo网络设备。
|
||
|
||
## 总结时刻
|
||
|
||
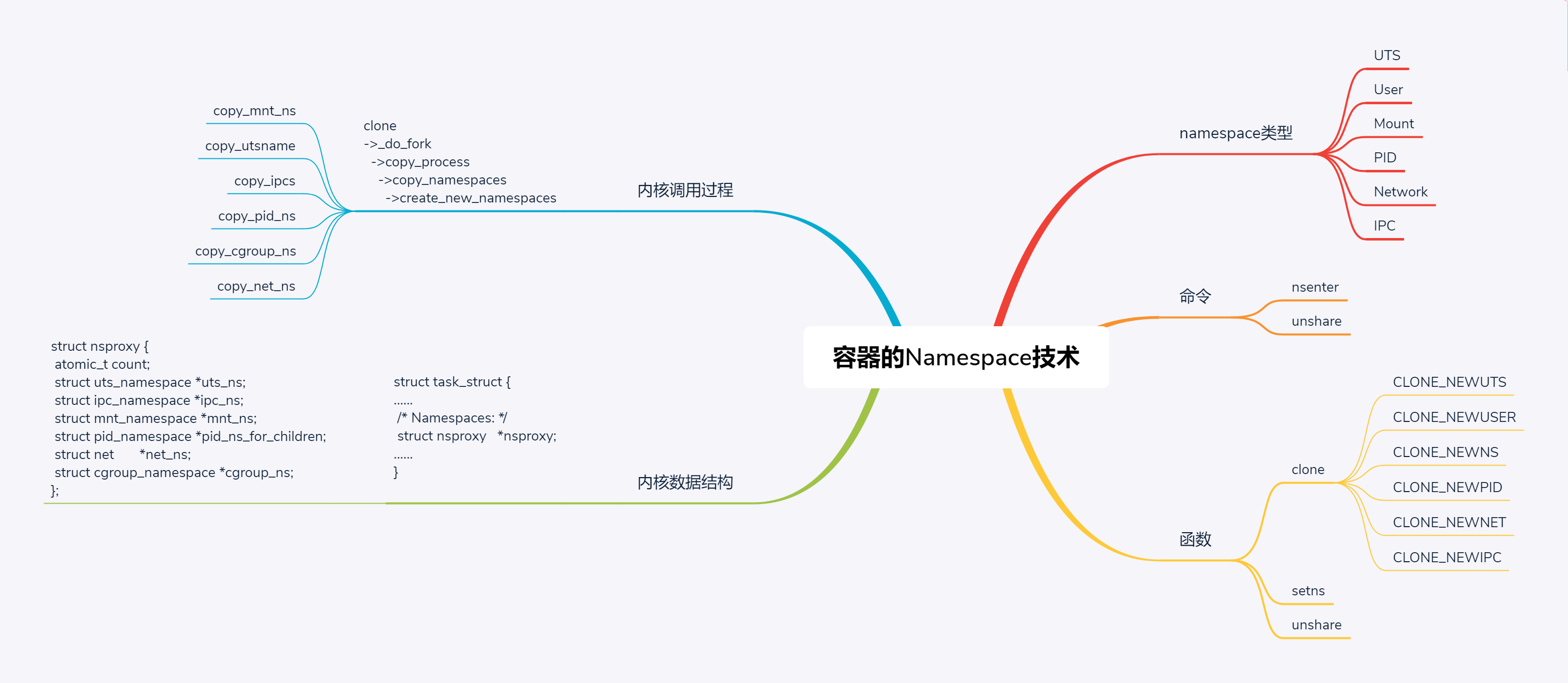
这一节我们讲了namespace相关的技术,有六种类型,分别是UTS、User、Mount、Pid、Network和IPC。
|
||
|
||
还有两个常用的命令nsenter和unshare,主要用于操作Namespace,有三个常用的函数clone、setns和unshare。
|
||
|
||
在内核里面,对于任何一个进程task\_struct来讲,里面都会有一个成员struct nsproxy,用于保存namespace相关信息,里面有 struct uts\_namespace、struct ipc\_namespace、struct mnt\_namespace、struct pid\_namespace、struct net \*net\_ns和struct cgroup\_namespace \*cgroup\_ns。
|
||
|
||
创建namespace的时候,我们在内核中会调用copy\_namespaces,调用顺序依次是copy\_mnt\_ns、copy\_utsname、copy\_ipcs、copy\_pid\_ns、copy\_cgroup\_ns和copy\_net\_ns,来复制namespace。
|
||
|
||
|
||
|
||
## 课堂练习
|
||
|
||
网络的Namespace有一个非常好的命令ip netns。请你研究一下这个命令,并且创建一个容器,用这个命令查看网络namespace。
|
||
|
||
欢迎留言和我分享你的疑惑和见解,也欢迎收藏本节内容,反复研读。你也可以把今天的内容分享给你的朋友,和他一起学习和进步。
|
||
|
||

|
||
|