15 KiB
29 | 渐入佳境:使用epoll和多线程模型
你好,我是盛延敏,这里是网络编程实战第29讲,欢迎回来。
在前面的第27讲和第28讲中,我介绍了基于poll事件分发的reactor反应堆模式,以及主从反应堆模式。我们知道,和poll相比,Linux提供的epoll是一种更为高效的事件分发机制。在这一讲里,我们将切换到epoll实现的主从反应堆模式,并且分析一下为什么epoll的性能会强于poll等传统的事件分发机制。
如何切换到epoll
我已经将所有的代码已经放置到GitHub上,你可以自行查看或下载。
我们的网络编程框架是可以同时支持poll和epoll机制的,那么如何开启epoll的支持呢?
lib/event_loop.c文件的event_loop_init_with_name函数是关键,可以看到,这里是通过宏EPOLL_ENABLE来决定是使用epoll还是poll的。
struct event_loop *event_loop_init_with_name(char *thread_name) {
...
#ifdef EPOLL_ENABLE
yolanda_msgx("set epoll as dispatcher, %s", eventLoop->thread_name);
eventLoop->eventDispatcher = &epoll_dispatcher;
#else
yolanda_msgx("set poll as dispatcher, %s", eventLoop->thread_name);
eventLoop->eventDispatcher = &poll_dispatcher;
#endif
eventLoop->event_dispatcher_data = eventLoop->eventDispatcher->init(eventLoop);
...
}
在根目录下的CMakeLists.txt文件里,引入CheckSymbolExists,如果系统里有epoll_create函数和sys/epoll.h,就自动开启EPOLL_ENABLE。如果没有,EPOLL_ENABLE就不会开启,自动使用poll作为默认的事件分发机制。
# check epoll and add config.h for the macro compilation
include(CheckSymbolExists)
check_symbol_exists(epoll_create "sys/epoll.h" EPOLL_EXISTS)
if (EPOLL_EXISTS)
# Linux下设置为epoll
set(EPOLL_ENABLE 1 CACHE INTERNAL "enable epoll")
# Linux下也设置为poll
# set(EPOLL_ENABLE "" CACHE INTERNAL "not enable epoll")
else ()
set(EPOLL_ENABLE "" CACHE INTERNAL "not enable epoll")
endif ()
但是,为了能让编译器使用到这个宏,需要让CMake往config.h文件里写入这个宏的最终值,configure_file命令就是起这个作用的。其中config.h.cmake是一个模板文件,已经预先创建在根目录下。同时还需要让编译器include这个config.h文件。include_directories可以帮我们达成这个目标。
configure_file(${CMAKE_CURRENT_SOURCE_DIR}/config.h.cmake
${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/include/config.h)
include_directories(${CMAKE_CURRENT_BINARY_DIR}/include)
这样,在Linux下,就会默认使用epoll作为事件分发。
那么前面的27讲和28讲中的程序案例如何改为使用poll的呢?
我们可以修改CMakeLists.txt文件,把Linux下设置为poll的那段注释下的命令打开,同时关闭掉原先设置为1的命令就可以了。 下面就是具体的示例代码。
# check epoll and add config.h for the macro compilation
include(CheckSymbolExists)
check_symbol_exists(epoll_create "sys/epoll.h" EPOLL_EXISTS)
if (EPOLL_EXISTS)
# Linux下也设置为poll
set(EPOLL_ENABLE "" CACHE INTERNAL "not enable epoll")
else ()
set(EPOLL_ENABLE "" CACHE INTERNAL "not enable epoll")
endif (
不管怎样,现在我们得到了一个Linux下使用epoll作为事件分发的版本,现在让我们使用它来编写程序吧。
样例程序
我们的样例程序和第28讲的一模一样,只是现在我们的事件分发机制从poll切换到了epoll。
#include <lib/acceptor.h>
#include "lib/common.h"
#include "lib/event_loop.h"
#include "lib/tcp_server.h"
char rot13_char(char c) {
if ((c >= 'a' && c <= 'm') || (c >= 'A' && c <= 'M'))
return c + 13;
else if ((c >= 'n' && c <= 'z') || (c >= 'N' && c <= 'Z'))
return c - 13;
else
return c;
}
//连接建立之后的callback
int onConnectionCompleted(struct tcp_connection *tcpConnection) {
printf("connection completed\n");
return 0;
}
//数据读到buffer之后的callback
int onMessage(struct buffer *input, struct tcp_connection *tcpConnection) {
printf("get message from tcp connection %s\n", tcpConnection->name);
printf("%s", input->data);
struct buffer *output = buffer_new();
int size = buffer_readable_size(input);
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
buffer_append_char(output, rot13_char(buffer_read_char(input)));
}
tcp_connection_send_buffer(tcpConnection, output);
return 0;
}
//数据通过buffer写完之后的callback
int onWriteCompleted(struct tcp_connection *tcpConnection) {
printf("write completed\n");
return 0;
}
//连接关闭之后的callback
int onConnectionClosed(struct tcp_connection *tcpConnection) {
printf("connection closed\n");
return 0;
}
int main(int c, char **v) {
//主线程event_loop
struct event_loop *eventLoop = event_loop_init();
//初始化acceptor
struct acceptor *acceptor = acceptor_init(SERV_PORT);
//初始tcp_server,可以指定线程数目,这里线程是4,说明是一个acceptor线程,4个I/O线程,没一个I/O线程
//tcp_server自己带一个event_loop
struct TCPserver *tcpServer = tcp_server_init(eventLoop, acceptor, onConnectionCompleted, onMessage,
onWriteCompleted, onConnectionClosed, 4);
tcp_server_start(tcpServer);
// main thread for acceptor
event_loop_run(eventLoop);
}
关于这个程序,之前一直没有讲到的部分是缓冲区对象buffer。这其实也是网络编程框架应该考虑的部分。
我们希望框架可以对应用程序封装掉套接字读和写的部分,转而提供的是针对缓冲区对象的读和写操作。这样一来,从套接字收取数据、处理异常、发送数据等操作都被类似buffer这样的对象所封装和屏蔽,应用程序所要做的事情就会变得更加简单,从buffer对象中可以获取已接收到的字节流再进行应用层处理,比如这里通过调用buffer_read_char函数从buffer中读取一个字节。
另外一方面,框架也必须对应用程序提供套接字发送的接口,接口的数据类型类似这里的buffer对象,可以看到,这里先生成了一个buffer对象,之后将编码后的结果填充到buffer对象里,最后调用tcp_connection_send_buffer将buffer对象里的数据通过套接字发送出去。
这里像onMessage、onConnectionClosed几个回调函数都是运行在子反应堆线程中的,也就是说,刚刚提到的生成buffer对象,encode部分的代码,是在子反应堆线程中执行的。这其实也是回调函数的内涵,回调函数本身只是提供了类似Handlder的处理逻辑,具体执行是由事件分发线程,或者说是event loop线程发起的。
框架通过一层抽象,让应用程序的开发者只需要看到回调函数,回调函数中的对象,也都是如buffer和tcp_connection这样封装过的对象,这样像套接字、字节流等底层实现的细节就完全由框架来完成了。
框架帮我们做了很多事情,那这些事情是如何做到的?在第四篇实战篇,我们将一一揭开答案。如果你有兴趣,不妨先看看实现代码。
样例程序结果
启动服务器,可以从屏幕输出上看到,使用的是epoll作为事件分发器。
$./epoll-server-multithreads
[msg] set epoll as dispatcher, main thread
[msg] add channel fd == 5, main thread
[msg] set epoll as dispatcher, Thread-1
[msg] add channel fd == 9, Thread-1
[msg] event loop thread init and signal, Thread-1
[msg] event loop run, Thread-1
[msg] event loop thread started, Thread-1
[msg] set epoll as dispatcher, Thread-2
[msg] add channel fd == 12, Thread-2
[msg] event loop thread init and signal, Thread-2
[msg] event loop run, Thread-2
[msg] event loop thread started, Thread-2
[msg] set epoll as dispatcher, Thread-3
[msg] add channel fd == 15, Thread-3
[msg] event loop thread init and signal, Thread-3
[msg] event loop run, Thread-3
[msg] event loop thread started, Thread-3
[msg] set epoll as dispatcher, Thread-4
[msg] add channel fd == 18, Thread-4
[msg] event loop thread init and signal, Thread-4
[msg] event loop run, Thread-4
[msg] event loop thread started, Thread-4
[msg] add channel fd == 6, main thread
[msg] event loop run, main thread
开启多个telnet客户端,连接上该服务器, 通过屏幕输入和服务器端交互。
$telnet 127.0.0.1 43211
Trying 127.0.0.1...
Connected to 127.0.0.1.
Escape character is '^]'.
fafaf
snsns
^]
telnet> quit
Connection closed.
服务端显示不断地从epoll_wait中返回处理I/O事件。
[msg] epoll_wait wakeup, main thread
[msg] get message channel fd==6 for read, main thread
[msg] activate channel fd == 6, revents=2, main thread
[msg] new connection established, socket == 19
connection completed
[msg] epoll_wait wakeup, Thread-1
[msg] get message channel fd==9 for read, Thread-1
[msg] activate channel fd == 9, revents=2, Thread-1
[msg] wakeup, Thread-1
[msg] add channel fd == 19, Thread-1
[msg] epoll_wait wakeup, Thread-1
[msg] get message channel fd==19 for read, Thread-1
[msg] activate channel fd == 19, revents=2, Thread-1
get message from tcp connection connection-19
afasf
[msg] epoll_wait wakeup, main thread
[msg] get message channel fd==6 for read, main thread
[msg] activate channel fd == 6, revents=2, main thread
[msg] new connection established, socket == 20
connection completed
[msg] epoll_wait wakeup, Thread-2
[msg] get message channel fd==12 for read, Thread-2
[msg] activate channel fd == 12, revents=2, Thread-2
[msg] wakeup, Thread-2
[msg] add channel fd == 20, Thread-2
[msg] epoll_wait wakeup, Thread-2
[msg] get message channel fd==20 for read, Thread-2
[msg] activate channel fd == 20, revents=2, Thread-2
get message from tcp connection connection-20
asfasfas
[msg] epoll_wait wakeup, Thread-2
[msg] get message channel fd==20 for read, Thread-2
[msg] activate channel fd == 20, revents=2, Thread-2
connection closed
[msg] epoll_wait wakeup, main thread
[msg] get message channel fd==6 for read, main thread
[msg] activate channel fd == 6, revents=2, main thread
[msg] new connection established, socket == 21
connection completed
[msg] epoll_wait wakeup, Thread-3
[msg] get message channel fd==15 for read, Thread-3
[msg] activate channel fd == 15, revents=2, Thread-3
[msg] wakeup, Thread-3
[msg] add channel fd == 21, Thread-3
[msg] epoll_wait wakeup, Thread-3
[msg] get message channel fd==21 for read, Thread-3
[msg] activate channel fd == 21, revents=2, Thread-3
get message from tcp connection connection-21
dfasfadsf
[msg] epoll_wait wakeup, Thread-1
[msg] get message channel fd==19 for read, Thread-1
[msg] activate channel fd == 19, revents=2, Thread-1
connection closed
[msg] epoll_wait wakeup, main thread
[msg] get message channel fd==6 for read, main thread
[msg] activate channel fd == 6, revents=2, main thread
[msg] new connection established, socket == 22
connection completed
[msg] epoll_wait wakeup, Thread-4
[msg] get message channel fd==18 for read, Thread-4
[msg] activate channel fd == 18, revents=2, Thread-4
[msg] wakeup, Thread-4
[msg] add channel fd == 22, Thread-4
[msg] epoll_wait wakeup, Thread-4
[msg] get message channel fd==22 for read, Thread-4
[msg] activate channel fd == 22, revents=2, Thread-4
get message from tcp connection connection-22
fafaf
[msg] epoll_wait wakeup, Thread-4
[msg] get message channel fd==22 for read, Thread-4
[msg] activate channel fd == 22, revents=2, Thread-4
connection closed
[msg] epoll_wait wakeup, Thread-3
[msg] get message channel fd==21 for read, Thread-3
[msg] activate channel fd == 21, revents=2, Thread-3
connection closed
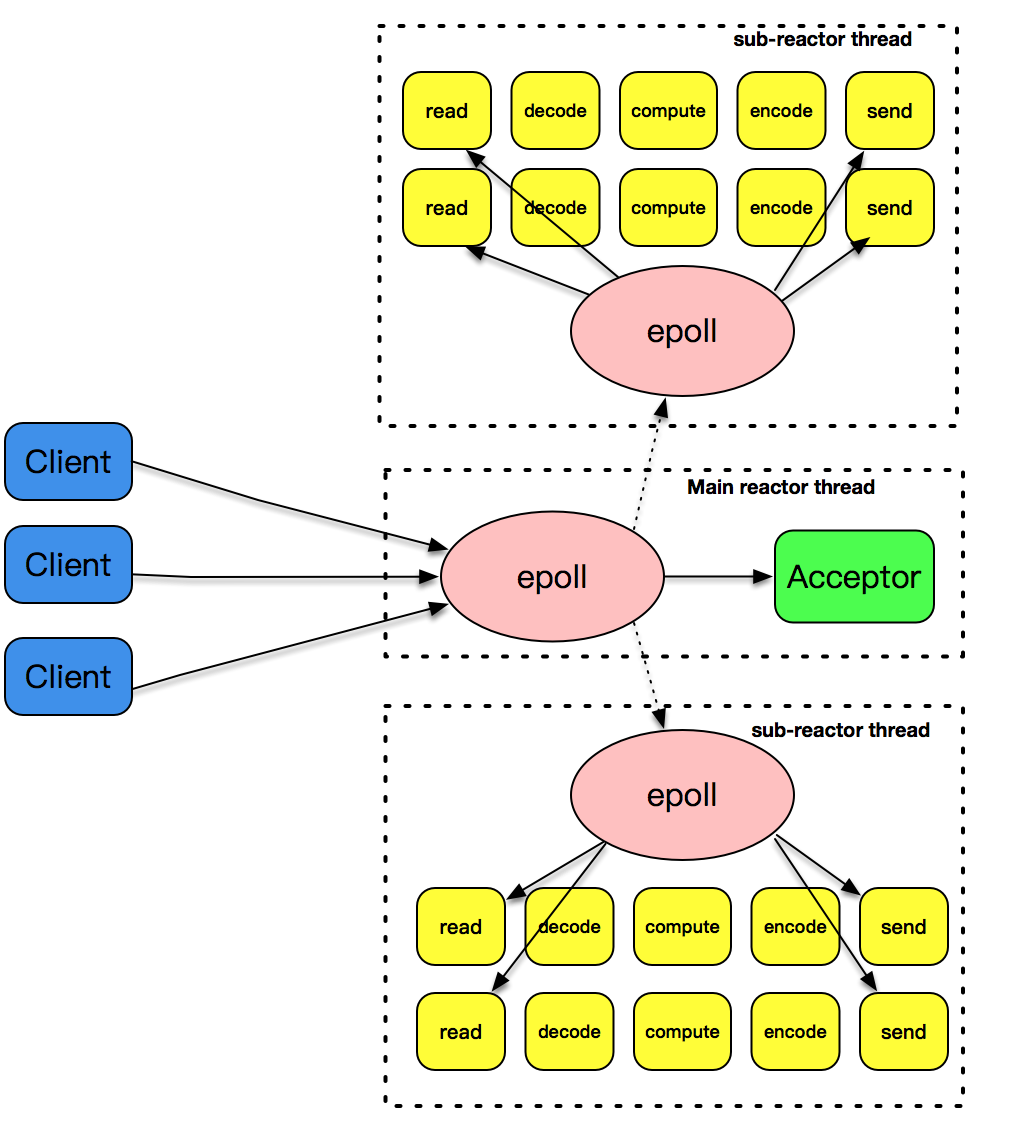
其中主线程的epoll_wait只处理acceptor套接字的事件,表示的是连接的建立;反应堆子线程的epoll_wait主要处理的是已连接套接字的读写事件。这幅图详细解释了这部分逻辑。
epoll的性能分析
epoll的性能凭什么就要比poll或者select好呢?这要从两个角度来说明。
第一个角度是事件集合。在每次使用poll或select之前,都需要准备一个感兴趣的事件集合,系统内核拿到事件集合,进行分析并在内核空间构建相应的数据结构来完成对事件集合的注册。而epoll则不是这样,epoll维护了一个全局的事件集合,通过epoll句柄,可以操纵这个事件集合,增加、删除或修改这个事件集合里的某个元素。要知道在绝大多数情况下,事件集合的变化没有那么的大,这样操纵系统内核就不需要每次重新扫描事件集合,构建内核空间数据结构。
第二个角度是就绪列表。每次在使用poll或者select之后,应用程序都需要扫描整个感兴趣的事件集合,从中找出真正活动的事件,这个列表如果增长到10K以上,每次扫描的时间损耗也是惊人的。事实上,很多情况下扫描完一圈,可能发现只有几个真正活动的事件。而epoll则不是这样,epoll返回的直接就是活动的事件列表,应用程序减少了大量的扫描时间。
此外, epoll还提供了更高级的能力——边缘触发。第23讲通过一个直观的例子,讲解了边缘触发和条件触发的区别。
这里再举一个例子说明一下。
如果某个套接字有100个字节可以读,边缘触发(edge-triggered)和条件触发(level-triggered)都会产生read ready notification事件,如果应用程序只读取了50个字节,边缘触发就会陷入等待;而条件触发则会因为还有50个字节没有读取完,不断地产生read ready notification事件。
在条件触发下(level-triggered),如果某个套接字缓冲区可以写,会无限次返回write ready notification事件,在这种情况下,如果应用程序没有准备好,不需要发送数据,一定需要解除套接字上的ready notification事件,否则CPU就直接跪了。
我们简单地总结一下,边缘触发只会产生一次活动事件,性能和效率更高。不过,程序处理起来要更为小心。
总结
本讲我们将程序框架切换到了epoll的版本,和poll版本相比,只是底层的框架做了更改,上层应用程序不用做任何修改,这也是程序框架强大的地方。和poll相比,epoll从事件集合和就绪列表两个方面加强了程序性能,是Linux下高性能网络程序的首选。
思考题
最后我给你布置两道思考题:
第一道,说说你对边缘触发和条件触发的理解。
第二道,对于边缘触发和条件触发,onMessage函数处理要注意什么?
欢迎你在评论区写下你的思考,也欢迎把这篇文章分享给你的朋友或者同事,一起交流进步。